Astrophotography
Welcome to !astrophotography!
We are Lemmy's dedicated astrophotography community!
If you want to see or post pictures of space taken by amateurs using amateur level equipment, this is the place for you!
If you want to learn more about taking astro photos, check out our wiki or our discord!
Please read the rules before you post! It is your responsibility to be aware of current rules. Failure to be aware of current rules may result in your post being removed without warning at moderator discretion.
Rules
- I | Real space images only.
-
Astrophotography refers to images of astronomical objects or phenomena exclusively.
-
~~Images that show objects or people below the Kármán Line (100km) will be removed.~~ We won't be enforcing this rule for now, but as the community grows eventually we will split and have a separate space for just landscape astro.
-
Images must be an accurate representation of a real astronomical object.
- II | Original and Amateur Content Only
-
Image posts can only be images that you have captured and processed yourself, or discussion about capturing and/or processing your own images.
-
Images acquired from public sources, professional observatories, or other professional services are not allowed.
-
If you have done a drastic alteration or reprocessing of a prior submission, you may repost your edit - but only after a minimum of one week has passed.
- III | Post Types
-
Image posts are to link directly to the image, not to landing pages, personal galleries, blogs, or professional sites. Link to these in the comments. (AstroBin and Imgur, are allowed)
-
Questions are welcome here for the time being.
-
Links to blogs, articles or external websites should be interesting and promote discussion about amateur astrophotography.
- IV | Titles
- All image posts should just include include the name of the object being photographed. Extra info such as equipment, it being your first image, or other information should go in a comment along with your acquisition info. Please see this page for more details.
If your post is removed, try reposting with a different title. Don't hesitate to message the mods if you still have questions!
- V | Acquisition and Processing Information
-
All submitted images must include acquisition and processing details as a top-level comment. All posts without this information may be given a warning, and if not updated will be removed.
-
This includes the telescope, mount, camera, accessories, and any other pieces of equipment you used to capture the image.
-
You must also include processing details, i.e. the programs you used and a general rundown of the workflow/processes you used within those programs. “Processed in Photoshop” is not enough.
view the rest of the comments
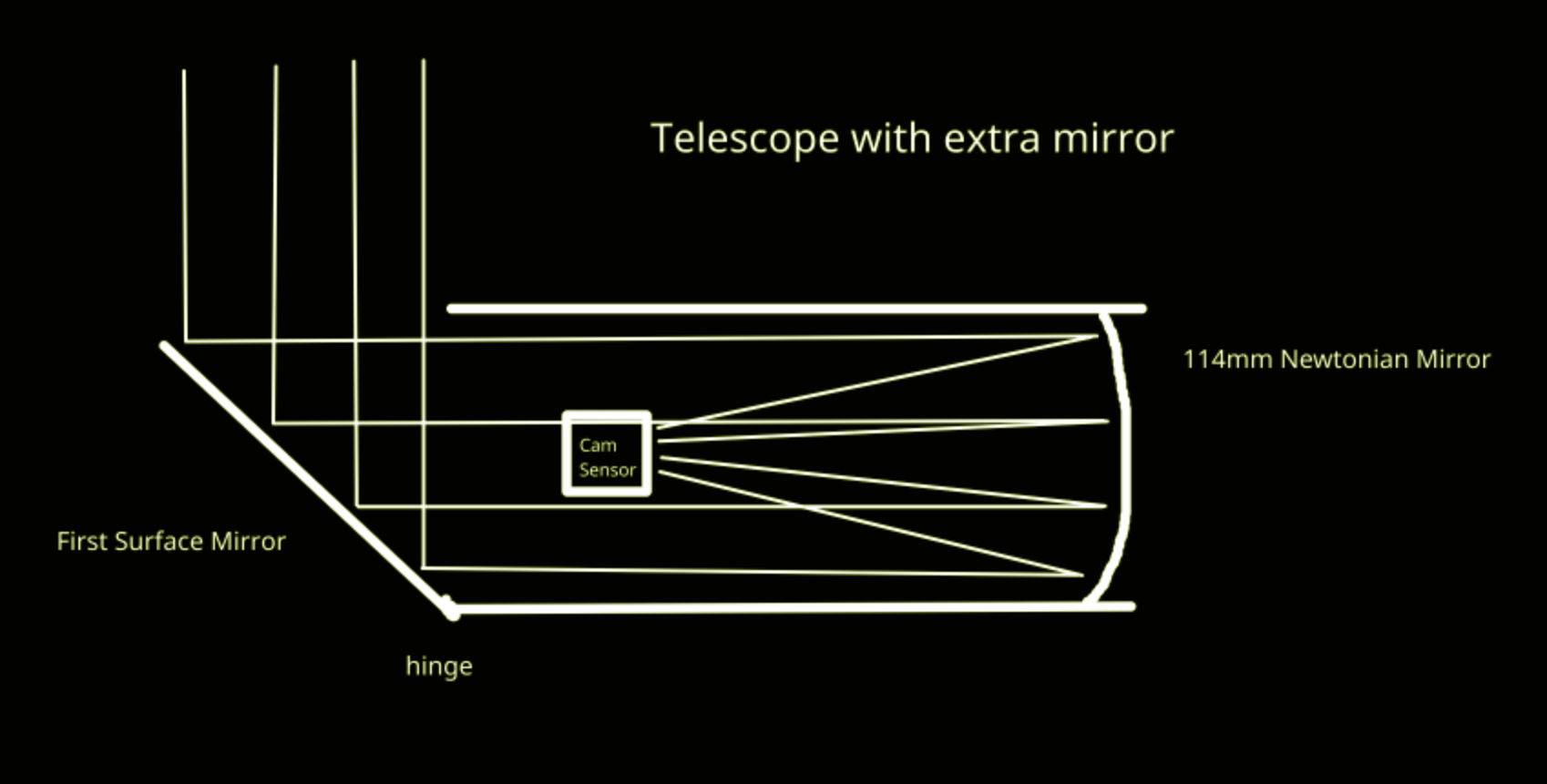
Flat mirrors are pretty easy to get right (no aspheres involved). Of course, you want a mirror reflecting from the front of the glass, not from the back like those you see every day.
I think your main problems are going to be practical: it now needs to be mounted differently, and it would be much harder to mount equatorial, so tracking is more difficult. You would probably have a problem with scattered light, as the entrance pupil isn't well defined, and there may be direct paths for light to get to the focal plane without going the route you've highlighted; that will make it much more difficult to do faint work, and I think it's the main problem you'll have.
oh right, i didnt thought about that, maybe i could add some sort of shroud to the light inlet
To be effective, it would have to be like a telescope tube, which is what you're trying to eliminate in the first place.
thats what i was thinking :/
Tubeless telescopes exist tho, i saw some big diy newtonians that did not have any
There are good reasons to not use a tube: tubes limit airflow over the mirror, increasing "mirror seeing", and they add weight. But then you need an alternative way of rejecting off-axis light. One way of doing that is a dome or similar enclosure.
Technically getting one surface flat is easy. Hell, it's one of the first thing you learn in measurement science (three plates and perfect smoothness). However a mirror isn't just about being flat, it is also about light reflection. And that makes it more interesting. In a perfect vacuum, you could do a silver mirror without the glass and have it be perfectly flat and not worry about oxidation. But the reality of making that mirror stay perfectly reflective means that glass or similar is usually involved. And then you move away from the perfect flatness problem (relatively easy) to perfectly parallel planes (significantly harder).
Furthermore, keeping a plane or surface perfectly.flat after manufacture requires uniform temperatures, which are rarely present in amateur telescopes.
The end result is almost always the introduction of additional error.