this post was submitted on 16 Jun 2024
267 points (92.9% liked)
Data Is Beautiful
6884 readers
244 users here now
A place to share and discuss data visualizations. #dataviz
(under new moderation as of 2024-01, please let me know if there are any changes you want to see!)
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
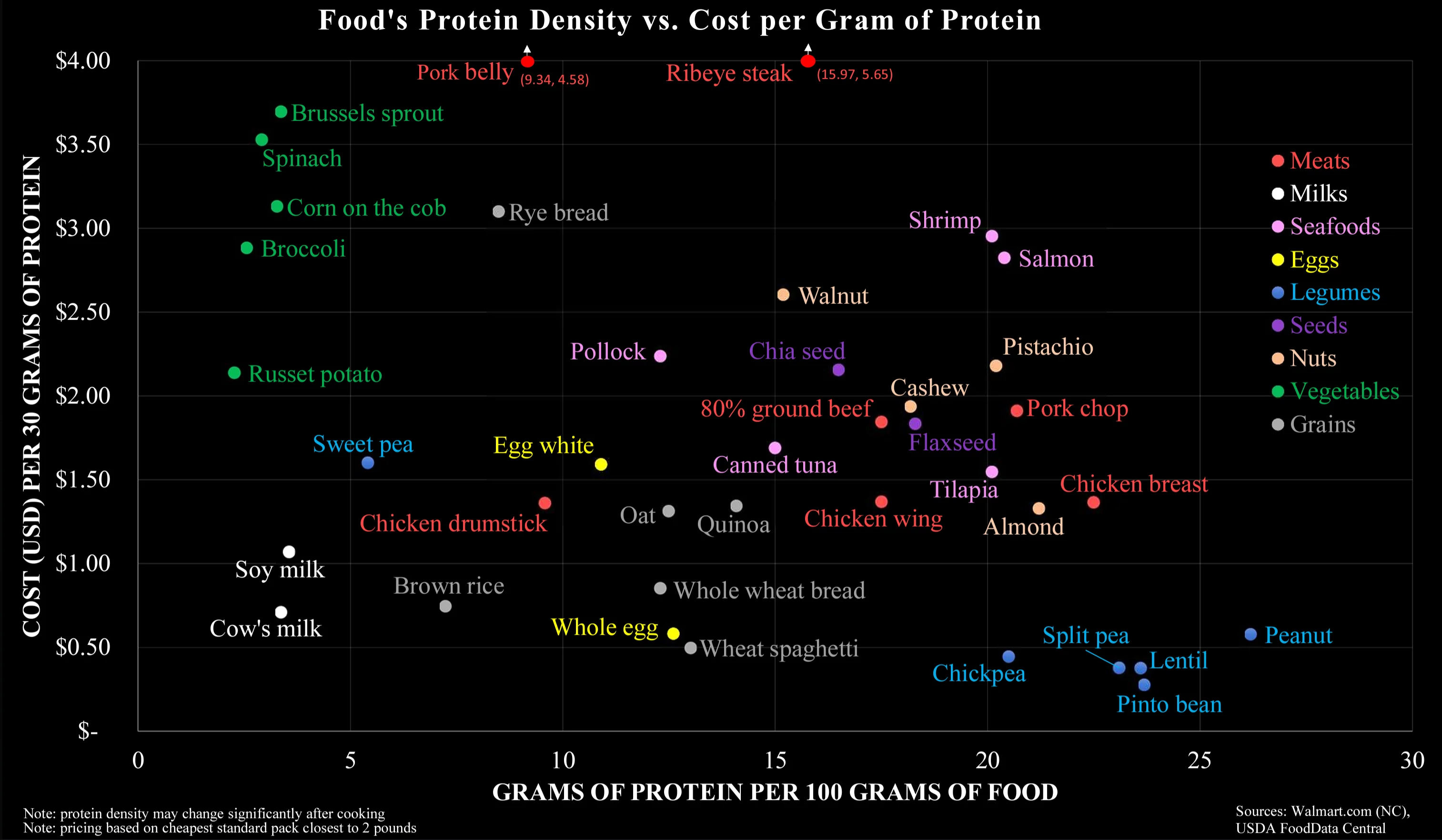
Most crucially, the graph is an oversimplification of protein content. Legumes do not contain the full amino acid chain unlike meat. Non-meats need to be evaluated with the nuance of its nutrients not necessarily being as bio-available for human digestion. Carrots and Vitamin A, for example.
Thank you for saying this. The PDCAAS shows the digestible properties of different protein sources. It would be a good multiplicative factor for the X-Axis to make the sources comparable, since Cow's Milk, Chicken, Egg, Whey, Casein, Tuna and Soy Protein (Isolate) have a score of 1 while Lentils, Tofu, Rice and Wheat have roughly 0,5.
That means you need to eat (and buy and cook) twice the amount of the latter to gain roughly the amount of actionable protein of the former.
I've had to debunk this myth multiple times in this post already, I'm not sure who started it. Legumes do have all the aminos and in sufficient amounts.
Also on bioavailability, it is a double edged sword. For example heme uptake is greater than mineral iron, but your body has very little control with inhibiting uptake when you already have adequate levels. With the mineral form your body has various ways to promote or inhibit uptake. The same is true of your example of vitamin A. You can pretty much eat as many carrots as you want and suffer no ill effects, eating too much liver or taking too many liver oil supplements however can lead to poisoning.