this post was submitted on 11 May 2024
217 points (98.2% liked)
Space
8746 readers
7 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
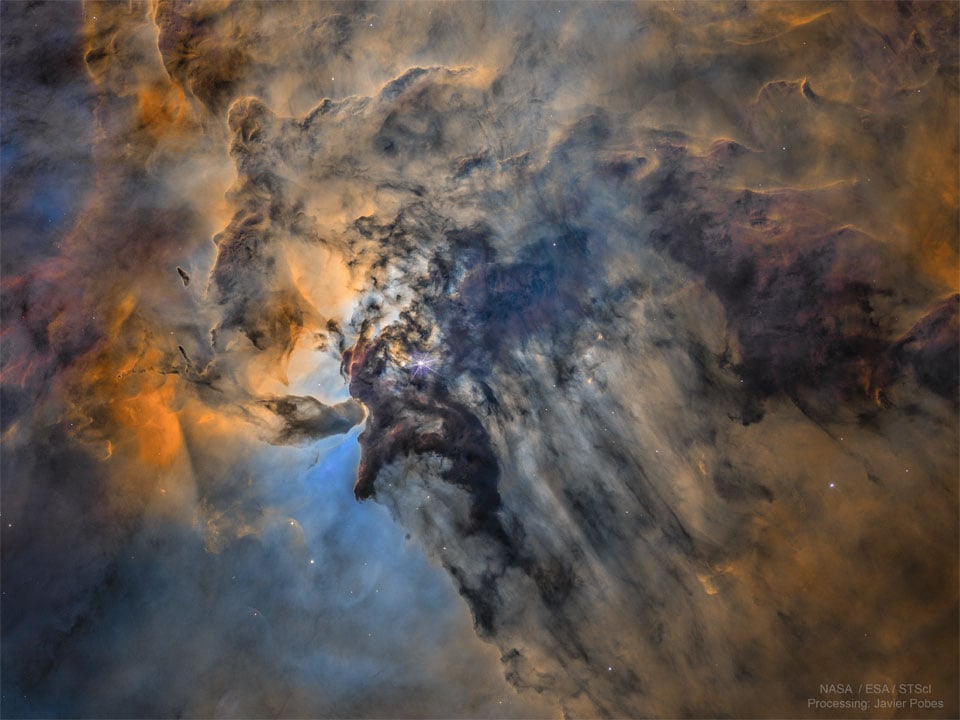 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

Sure, you won't reach 100%. But say you reach 99.9% - the Dyson sphere should radiate infrared at 0.1% of a normal star, right? It wouldn't necessarily be bright.
They must be mining a lot of bitcoin to need 99.9% of a star’s energy.
Or else to power one of those Kurtzgestat space lasers that will melt us anyway.
Maybe they are just fabricating matter. That takes a surprising amount of energy!
Even if that level of efficiency were possible, 0.01% of a star's output is still a substantial amount of heat. You would still have to radiate it away otherwise it would melt your mega structure, and you would have to radiate it out equally in all directions otherwise you'd knock it off its orbit with the thrust generated from the radiating of the heat on one side.
Yeah, it’s interesting to think about IR powered thrust.
I wonder if moving a star by cooling one side could ever happen? Like in a some weird future tech way obviously.
Not all heat can be converted to work by the second law of thermodynamics. Now the question is, how hot can the star be for it to sustain life? Can most of its light be UV with very little visible? https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-physics/chapter/15-4-carnots-perfect-heat-engine-the-second-law-of-thermodynamics-restated/