Technology
This is the official technology community of Lemmy.ml for all news related to creation and use of technology, and to facilitate civil, meaningful discussion around it.
Ask in DM before posting product reviews or ads. All such posts otherwise are subject to removal.
Rules:
1: All Lemmy rules apply
2: Do not post low effort posts
3: NEVER post naziped*gore stuff
4: Always post article URLs or their archived version URLs as sources, NOT screenshots. Help the blind users.
5: personal rants of Big Tech CEOs like Elon Musk are unwelcome (does not include posts about their companies affecting wide range of people)
6: no advertisement posts unless verified as legitimate and non-exploitative/non-consumerist
7: crypto related posts, unless essential, are disallowed
view the rest of the comments
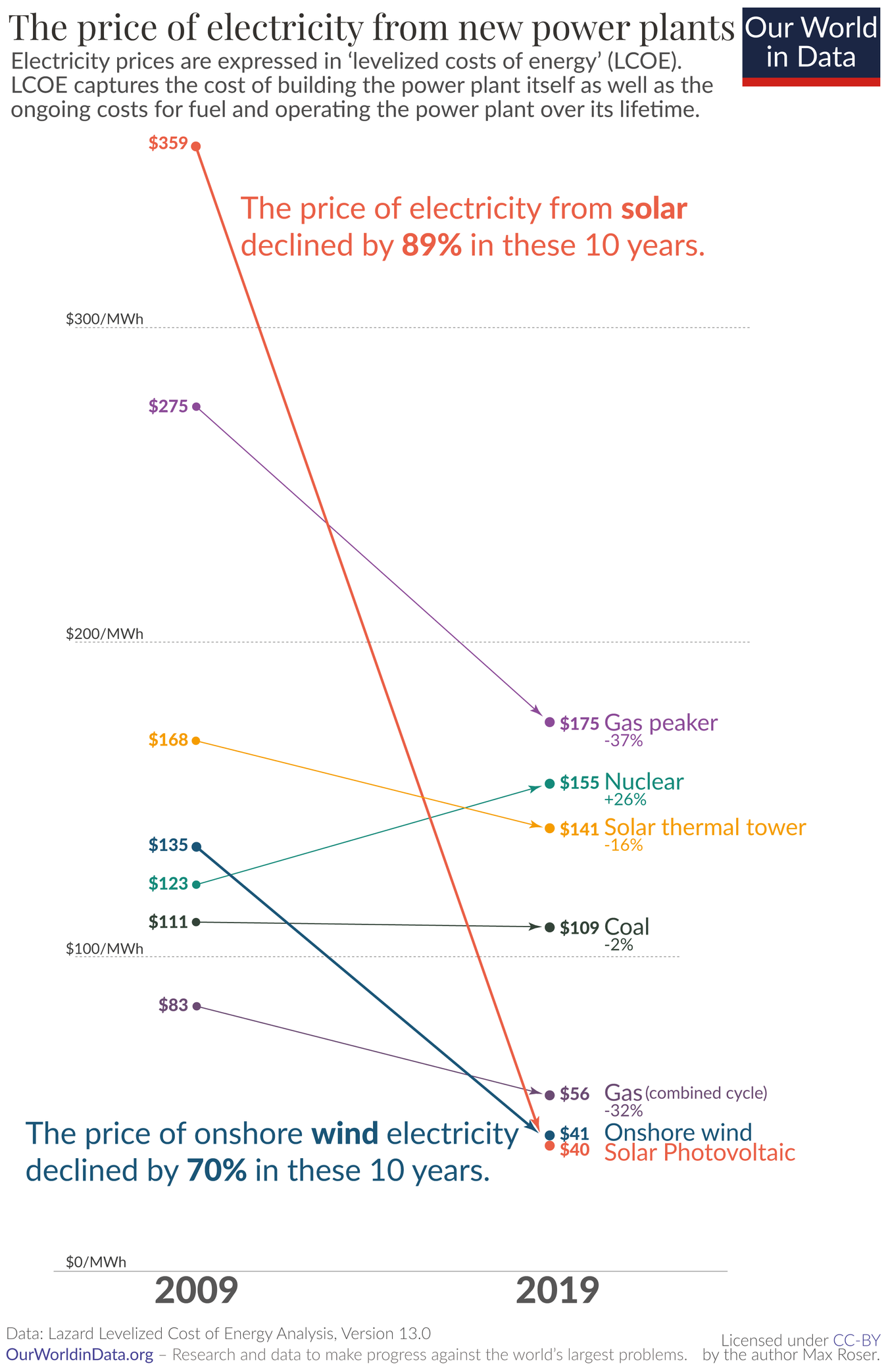
The problem right now is that we need to find better ways to turn renewable energy into stable, reliable power. The power production problem is highly dependent on balancing power generation and demand, and any excess energy must be stored, used, or wasted.
The main benefit of gas/coal/etc. is that we can (almost) always control the output to a close margin based off of demand projections, which are typically updated every 15 minutes. That being said, the drawbacks of using this form of generation are obvious and need to be addressed.
For renewables like solar and wind, we can't always predict the output, so in the larger scale of power balance, we need to supplement it with something that can make up for fluctuations in generation. In the current system, this is from conventional sources.
The goal is to implement a robust energy storage system, ideally one that can hold a huge amount of excess renewable power during the day (largely due to solar), and reliable output that power when it is needed (higher demand at night). I would love to see the day where our nation is fully powered by renewables, and I'm super happy to see that there have been pushes to build up renewables, but the target scenario relies on big advancements in storage.
I would suggest anyone who is interested in what I said to look up "california duck curve solar" for some reading on what challenges solar overgen presents in bright and sunny states.
All that being said... we can do it! I sincerely hope we reach a point where we can phase out dirty generation across the globe, but it will take a lot of time and effort.
source: taking several power systems courses as part of my EE degree
Agreed. This is spending that our country isn't willing to do, mostly because of what we already have (both in terms of infrastructure and in political influence). Personally, I hate this.
As for Cali's duck curve issue, desalination is a great idea, but expansion of renewables and storage should really come first. Keep in mind that the current Cali grid generates much less dirty power during the day, where solar covers a majority of demand. Should we divert that solar power to desalination, we would need to ramp up dirty power generation during the day, and we would continue to generate dirty power at night.
While I agree with you, we also have to consider what this would do at scale. The 70% of excess power that you lose here translates to wear on the solar panel systems that is never realized into power. That is, the systems will wear at the same rate, but the amount of power you can utilize over the lifespan of the systems is decreased. It's still a better solution than not implementing these at all, but I'd be wary as to how reluctant our society would be to the spending, especially if the ratio of cost to utilization(?) becomes skewed.
Well, that's an issue in of itself. It'd be great if we could waste less power in conventional generation, but it'd be even better if we could match or even beat that with renewables. I hope we can reach a point where everyone can agree to implement renewables sooner than later, but I don't see dirty power's political influence allowing for changes until renewable is equal to or better than dirty power. Which sucks, but a lot about our political system sucks.
That's really more of an indictment on LA having too much parking than anything else.
Put the solar panels on the roofs. Replace the worthless parking lots with more productive buildings. And, obviously, quit forcing everybody to drive everywhere.
The whole base load situation is largely over hyped, as a diverse and slightly overbuilt network of renewable would compensate for fluctuations with minimal storage needed. Iirc you would just need 118% capacity with a 2 hour storage buffer to achieve stability rates on par with a traditional grid. And nuclears small footprint actually hinders it when filling a base load requirement, as nuclear provides a lot of power at a single location, but if you want to base load a national grid you want a little power at lots of locations. (Which can be argued that SMRs will fill that role, but that's a whole other argument)
What are SMRs?
Small modular reactors. It's an unproven technology that tech bros love to talk about like its magic and going to fix everything.