this post was submitted on 24 Jun 2024
107 points (98.2% liked)
[Dormant] moved to !space@mander.xyz
10577 readers
2 users here now
This community is dormant, please find us at !space@mander.xyz
You can find the original sidebar contents below:
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
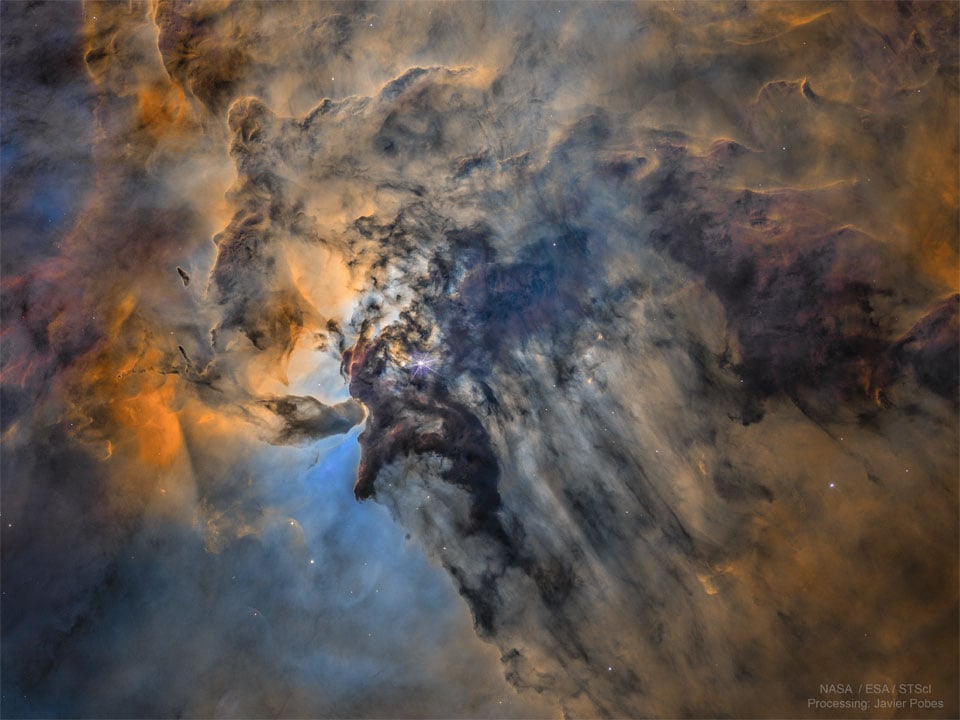 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
The thought of Quark Stars have fascinated me ever since I first read about them, about maybe fifteen years ago, a supernova remnant that is dense enough to overcome neutron degeneracy pressure, not dense enough to become a singularity.
The Cosmic Microwave Background was emitted when the Universe was around 370,000 years old, the oldest light in the Universe but the way space expands and accelerates, the distance at which the photons we detect now were emitted and when they reach us, is all distorted and crazily stretched. If you want to visualize how light moves as slow as a snail in the grand scheme of things, look no further.
Neutrinos, as far as we know the closest a particle with mass approaches zero, to the infinitesimal point that it's thought it doesn't derive its' mass from the Higgs Field. Then there's the as-yet elusive Cosmic Neutrino Background, emitted when the Universe was less than a second old.